Authentication Set Up
ASP.NET Core Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity is a membership framework that provides authentication and authorization services.
Check that your appliation has the necesasry package requirements
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
Managed through:
Users and Roles
The framework is build around users and roles. These are managed through the following classes:
IdentityUser: represents the user.IdentityRole: represents user roles.IdentityDbContext: a custum DbContext used to communicate with the user and role data.
Application Users and Roles
As the presence of the DbContext suggests, user and roles are Models. To create application specific models the framework classes of IdentityRole, IdentityUser and IdentityDbContext can be inherited.
AppIdentityUser
For our application create a AppIdentityUser class that inherits from the IdentityUser class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity namespace.
The IdentityUser provides core Properties such as UserName and Email. It can be extended to include custom Properies for example:
AppIdentityRole
For our application create AppIdentityRole class that inherits from the IdentityRole class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity namespace. It provides properties such as Name.
Again this can be extended to include custom Properies for example:
AppIdentityDbContext
A AppIdentityDbContext Class will be created for our application. This inherits from the framework's IdentityDbContext.
The AppIdentityDbContext is set up to communicate to the underlying user and role data store.
The AppIdentityDbContext class inherits from the IdentityDbContext<TUser,TRole,TKey> class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore namespace.
The TUser parameter indicates the type of application’s user (AppIdentityUser in this case).
The TRole parameter indicates the type of application’s role (AppIdentityRole in this case).
The TKey parameter indicates the type of the primary key for users and roles (string in this case).
The constructor of the AppIdentityDbContext class is designed for Dependency Injection support.
Configure the Start Up
Edit the ConfigureServices() method in the Startup.js file as follows using Dependency injection for the DbContext. Add the code below the existing AddDbContext for ApplicationDbContext:
Edit the Configure method as follows:
Set Up the Database
Entity Framework can set up the required tables for the Identity to work.
Via NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solutions ... install:
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
Use the console to run the migration command and then update the database
add-migration IdentityMigration -context AppIdentityDbContext
Update-Database
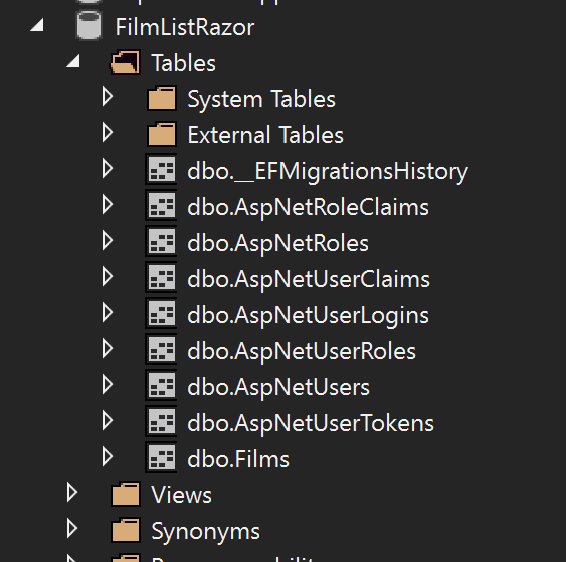
The following tables should now appear: