APIs
API Specific Projects
Visual Studio comes with a project template to create an application that just provides API Endpoints
Create a new project with:
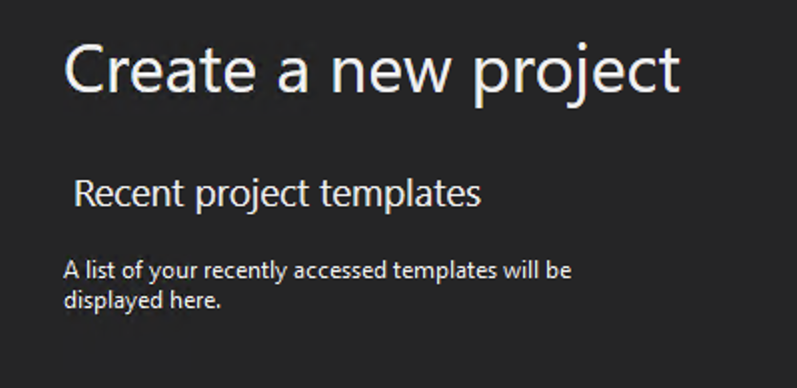
Select "ASP.NET Core Web Application" from the options available.

Name the Project "MyGameAPI".
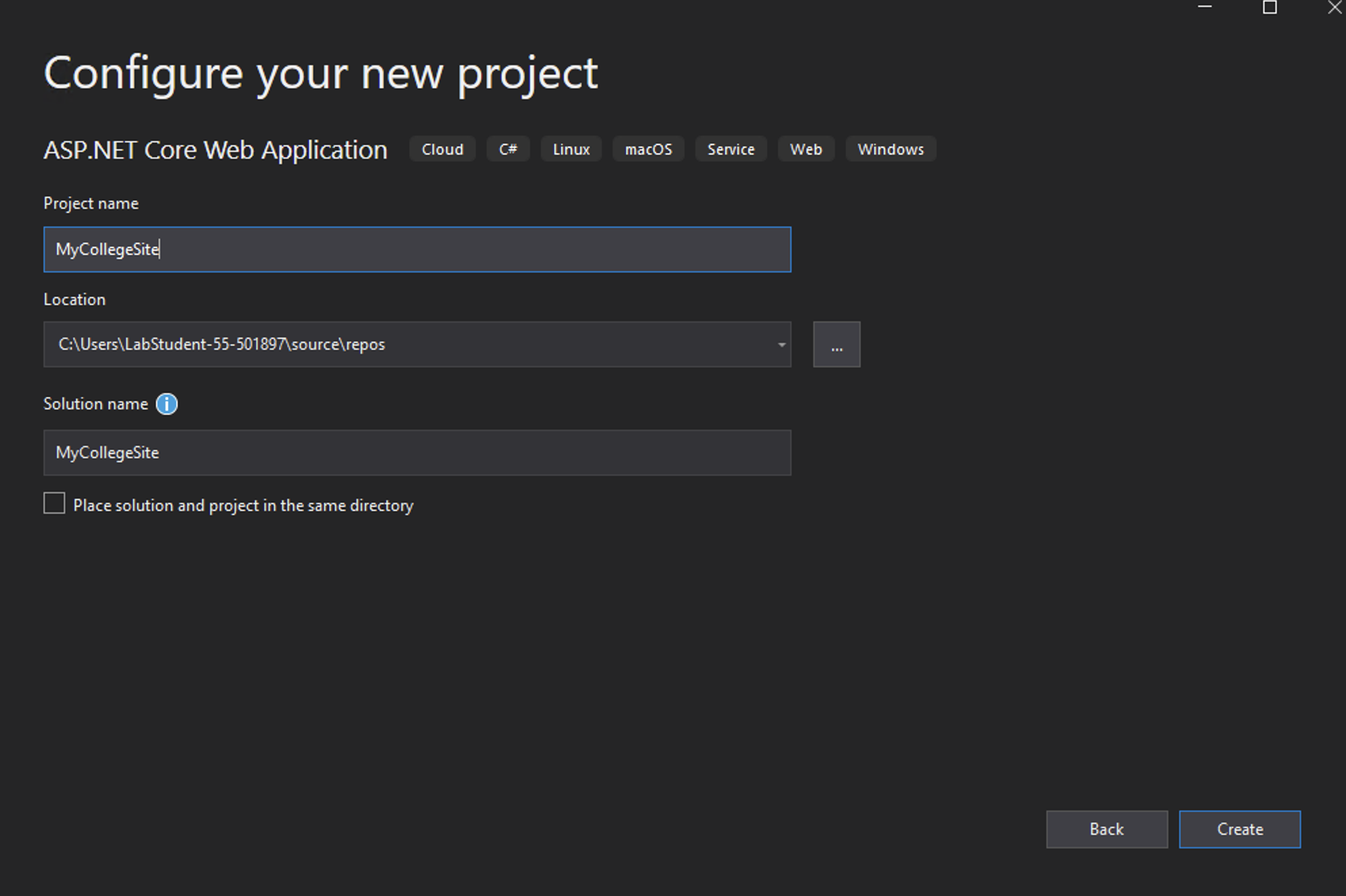
Select .NET Core from the drop-down and "API" from the list.
For this purposes of this lab uncheck Configure for HTTPS.
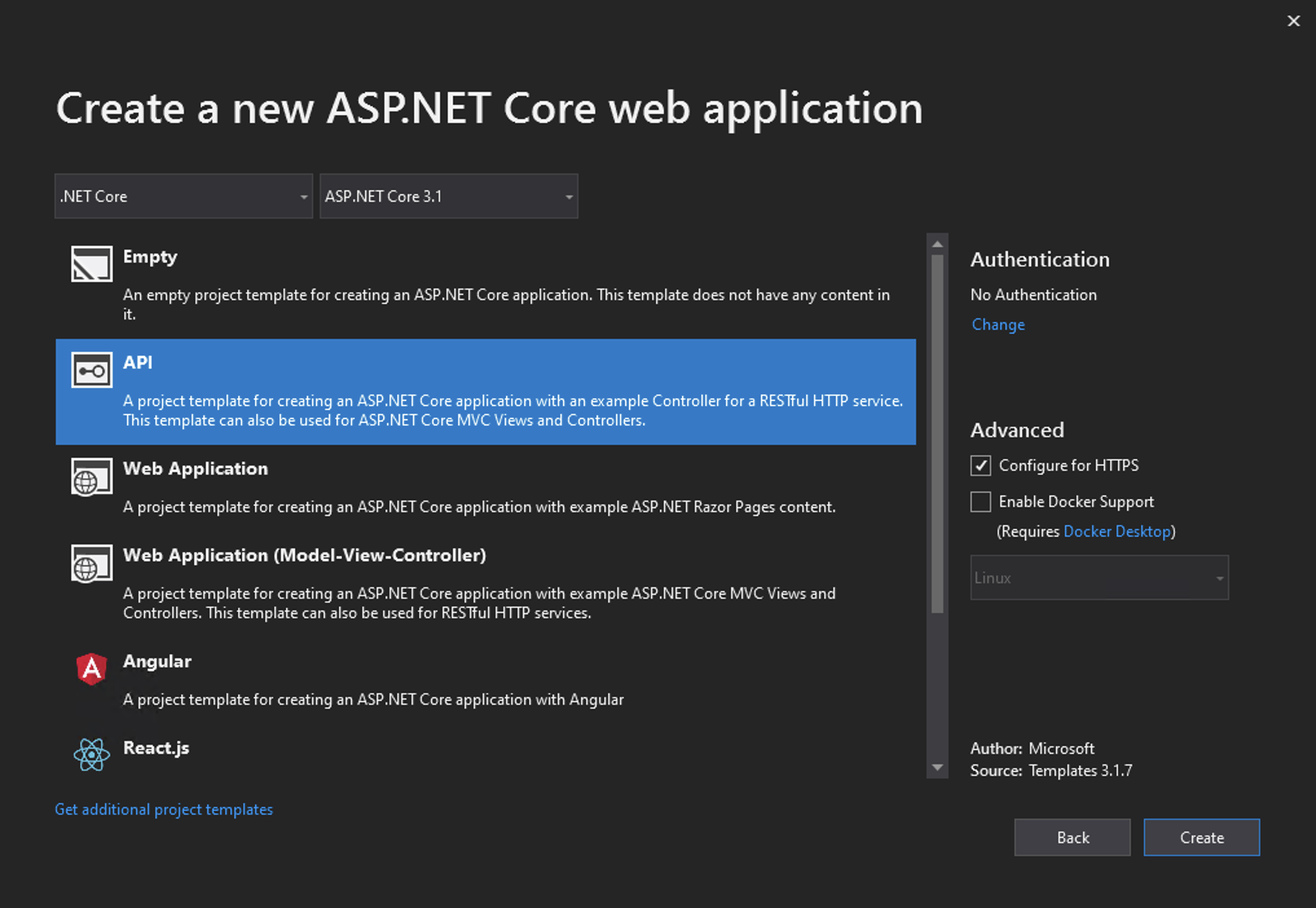
Exploring the Default API Application
Visual Studio creates a application themed around weather. The file structure is as follows:
Running the applicaiton will produce a the following:
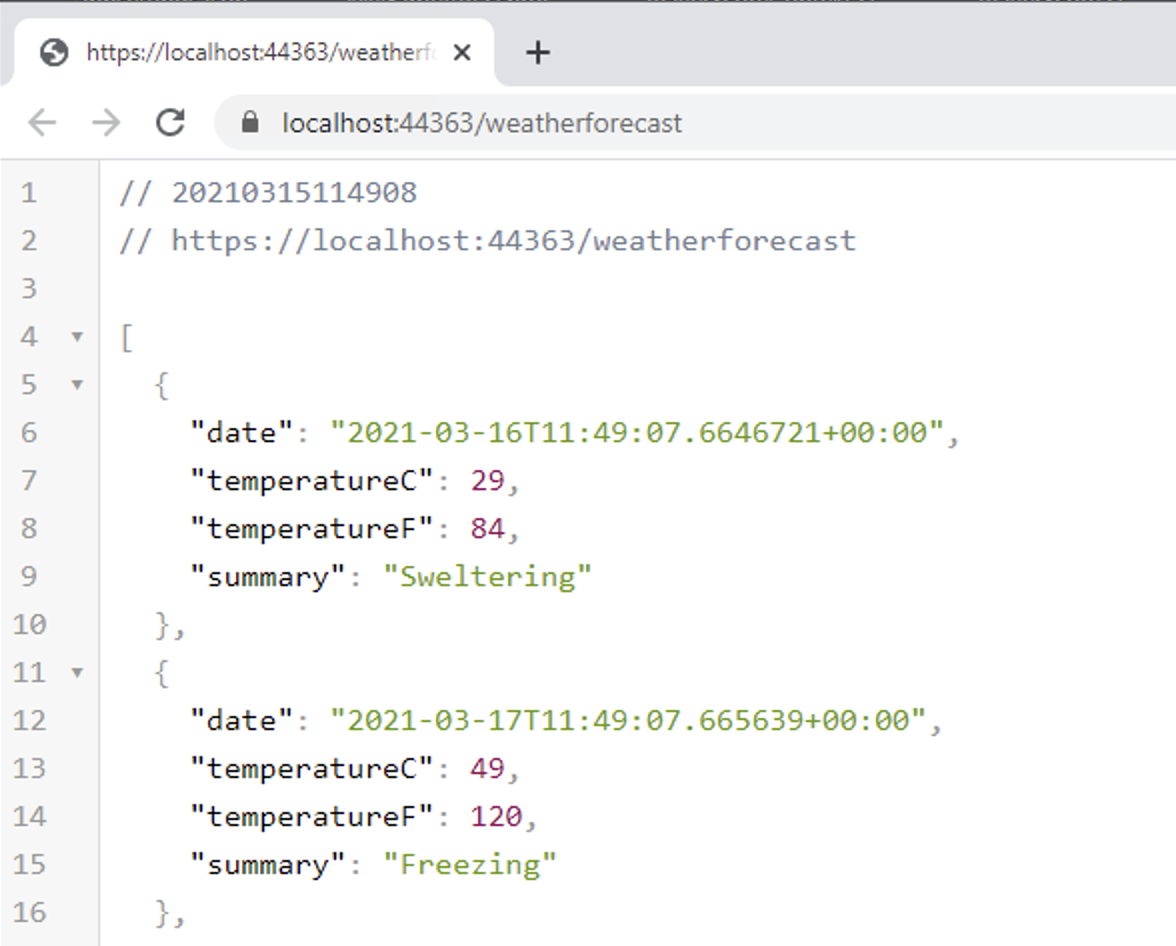
Note:
The above is the resulting of viewing the output in Google Chrome with the JSON formatter extension installed.
Exploring the Model, Startup.cs and Controller
The above output is based on WeatherForecast.cs Model located at the root of the application.
To see how the output was generated we'll begin with Startup. file. The file differs from the MVC project through the way Endpoints are set. As this is not a MVC application there is no default routing set out, instead endpoints are mapped by the controllers.
Open the Controllers/WeatherForecastController.cs file. The Controller has the attributes:
A technique known as Attribute Routing is used to creates routes of localhost:5000/api/Films for each of types of HTTP requests.
The [ApiController] attribute indicates that the controller responds to web API requests.
ASP.NET was designed for modern web experiences. Endpoints automatically serialize your classes to properly formatted JSON. One affect of this automatic serialization is that the Model is converted to camelCase, in that TemperatureC in the model becomes temperatureC in the JSON output.
As such the action:
... returns an IEnumberable serialized* to JSON. (The above action is called Get() purely because it makes sense to do so. It could be renamed to any other valid method name.)
* Serializing describes converting an object into a string. We serialize the C# IEnumerable into a string so that it can be transported via HTTP.