An Alternative Approach
Razor Pages
An alternative approach to MVC is to use ASP.NET Core Razor Pages. ASP.NET Core Razor Pages use a page-focused programming model where a Page .cshtml is associated with a PageModel .cshtml.cs. They are often described as been easier for newer developers to understand especially if they come from a PHP background.
Razor Pages File Structure
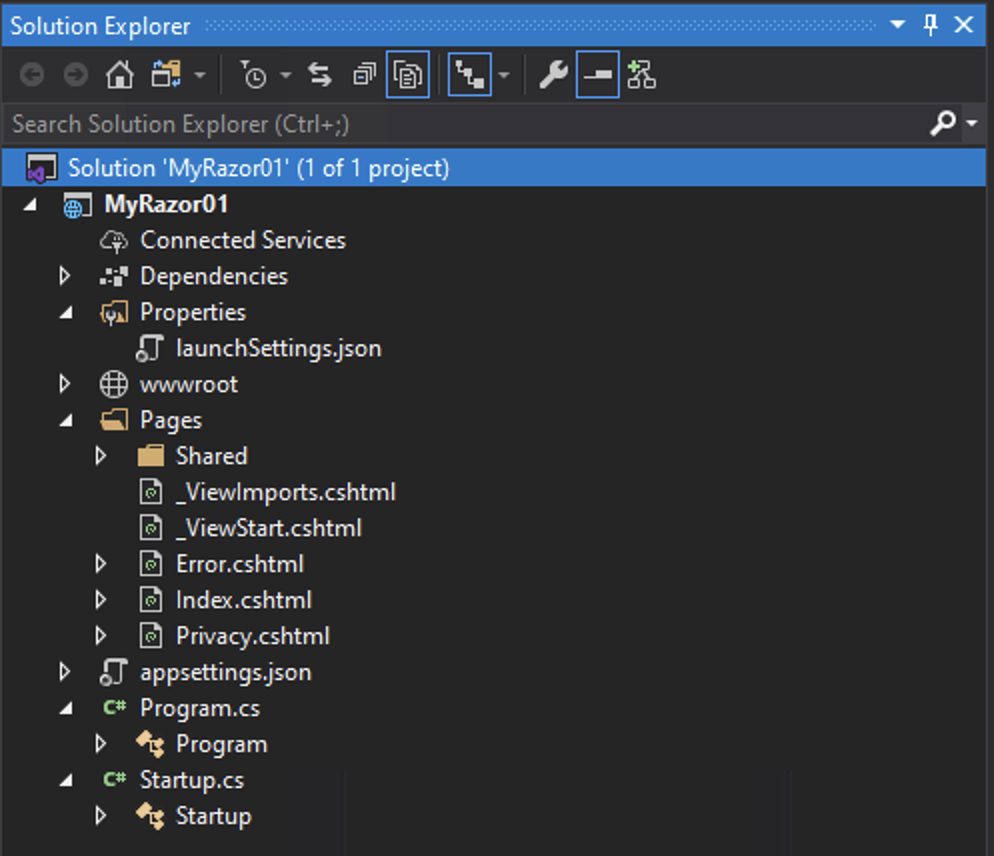
When setting up a Razor Pages Application the file structure is as follows:
The main folders are:
- wwwroot
-
Location of all 'static' files such as client side Javascript, images and CSS files. May also include HTML files that don't require any .net server side logic
- Pages
-
Location of the pages/views and their associated model pages. Each view Page .cshtml file has an associated PageModel .cshtml.cs that contains the logic for the page
The Shared folder contains the default layout inside _Layout.cshtml as well as partial pages to make page management easier and more modular.
My default the starter template makes use of the Bootstrap CSS Framework via a full path link in _Layout.cshtml.
As a developer you can choose to make more folders inside Pages to help structure your content.
Other core files will be familar from MVC applications but with some subtle differences. The familiar files are:
- appsettings.json
-
For application settings. Is used to store database connection strings.
- Program.cs
-
The main gateway to the application that holds the c#
Mainmethod. This calls Startup.cs - Startup.cs
-
Configures the application using Dependency Injection and controls the order of the middleware methods to be run.
The Startup.cs File with Razor Pages
It is in the Startup.cs that differences with the MVC approach can be found.
First in the ConfigureService() method services.AddRazorPages() is used to indicate a Razor Pages applications.
Second in the Configure() the app.UseEndpoints() does not make use of MapControllerRoute but uses the MapRazorPages() method instead.
Note:
There are no Controllers with this approach just Pages and PageModels. Each Page has its own PageModel.
When working with data we'll create a standard data Model in the same way as in a MVC application.
Getting Started with Razor Pages
Create a new project with:
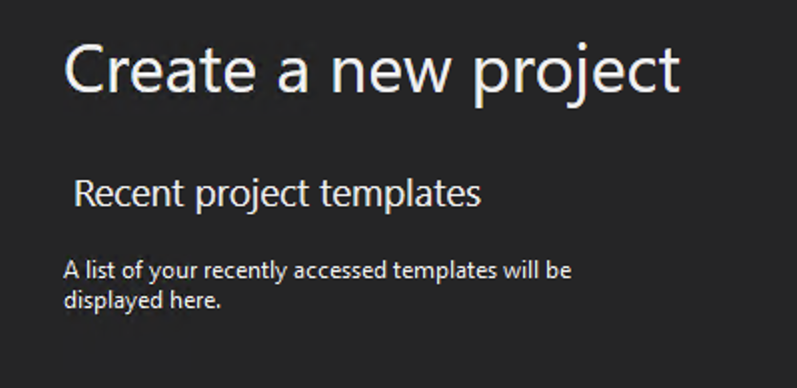
Select "ASP.NET Core Web Application" from the options available.

Give the project a name.
Select .NET Core from the drop-down and "Web Application" from the list.
Click "Create" and a a basic application is built for you. Run it via the IIS Express button.
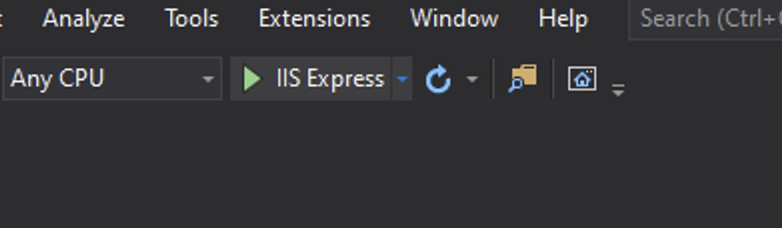
In your web browser your page can be viewed. It creates the starter application using Bootstrap CSS as with the MVC Project Template.
In the Solution Explorer the file structure outlined above can be seen:
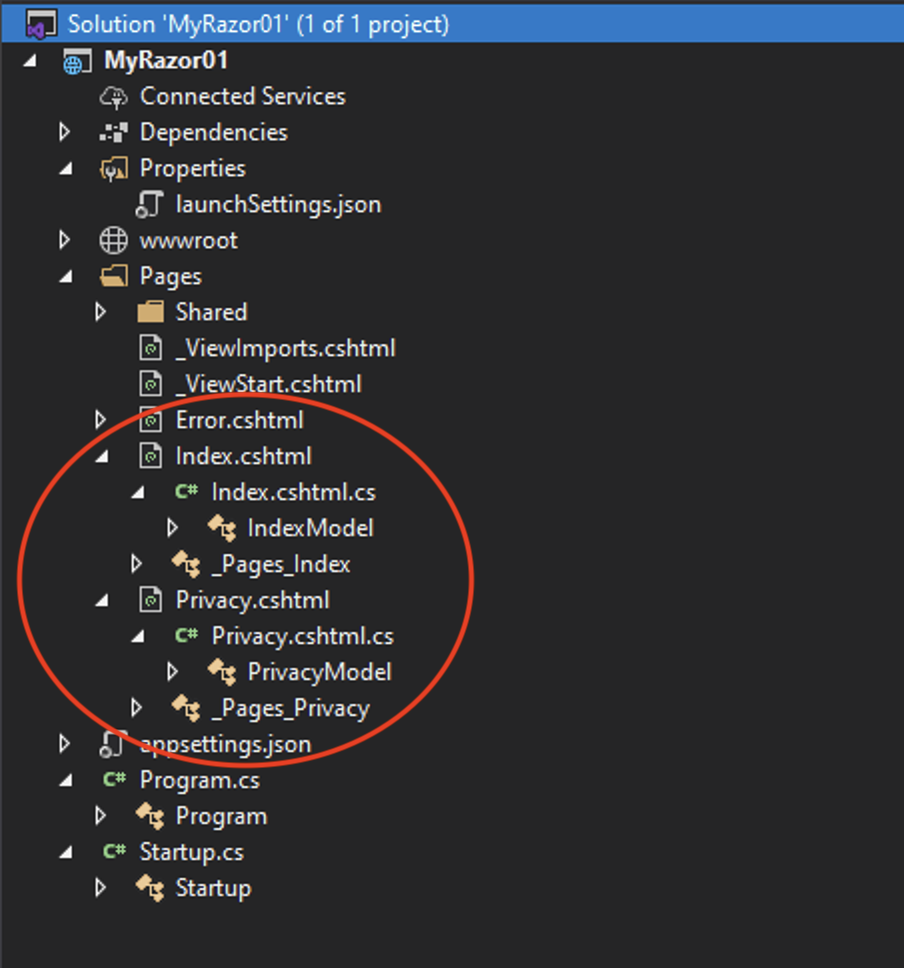
Explore the file structure to see how the Page Pages/Index.cshtml has a PageModel of Pages/Index.chtml.cs, and that the Page Pages/Privacy.cshtml has a Page Model of Pages/Privacy.chtml.cs.
Notice how the Routing differs from a MVC application because of the lack of controller.
| URL Called | Page Called | PageModel Called |
|---|---|---|
| localhost:5001/ | Pages/Index.cshtml | Pages/Index.cshtml.cs |
| localhost:5001/Privacy | Pages/Privacy.cshtml | Pages/Privacy.cshtml.cs |