Identity Set Up
This document references a Repo found on GitHub at:
Fork or Clone the Repo to experiment locally with the Project in Visual Studio.
Supporting Video: ASP.Net Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity is a membership framework that provides authentication and authorization services. When used with Entity Framework it will create a database table structure to support authentication and authorization functionality. It also offers a range of methods for user registration, sign-in, sign-out functionality with passwords securely encrypted.
- Authentication
- The process of identifying users and validating who they claim to be, most commonly via a username/password combination.
- Authorization
- Once a user's identity has been successfully authenticated, they can be authorized to use certain features of an application. Authorization is often role based ie - User, Manager, SuperUser etc.
Package Requirment for Identity Entity Framework
Check that your appliation has the necesasry package requirements.
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore
Managed through:
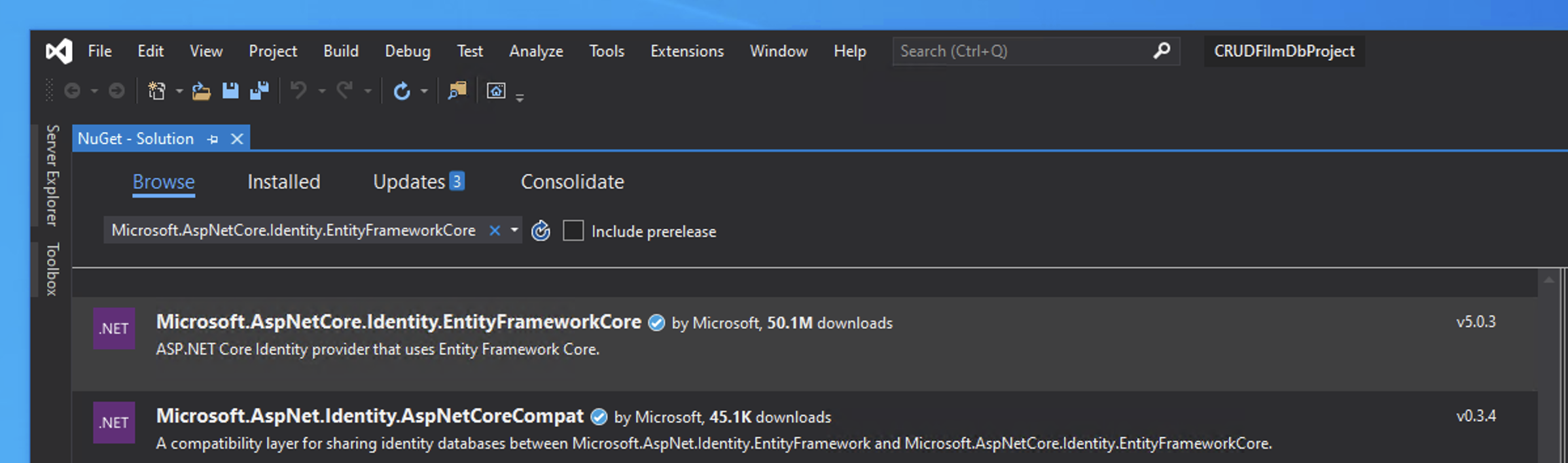
Take care to match your current Version of .Net Core.
Users and Roles
The framework is build around users and roles. These are managed through the following classes:
IdentityUser: represents the user.IdentityRole: represents user roles.IdentityDbContext: a customDbContextused to communicate with the user and role data.
Application Users and Roles
As the presence of the DbContext suggests, user and roles are Models. To create application specific models the framework classes of IdentityRole, IdentityUser and IdentityDbContext can be inherited.
AppIdentityUser
For our application create a AppIdentityUser class that inherits from the IdentityUser class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity namespace.
Create a class at Security/AppIdentityUser.cs as follows:
The IdentityUser provides core Properties such as UserName and Email. It can be extended to include custom properies for example:
AppIdentityRole
For our application create an AppIdentityRole class that inherits from the IdentityRole class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity namespace. It provides properties such as Name.
Create a class at Security/AppIdentityRole.cs as follows:
Again this can be extended to include custom properies for example:
AppIdentityDbContext
To manage the data required for securing our application an AppIdentityDbContext Class will be created. This inherits from the framework's IdentityDbContext.
Create a class at Security/AppIdentityDbContext.cs as follows:
Ensure that the class has access to the following packages:
The AppIdentityDbContext is set up to communicate to the underlying user and role data store.
The AppIdentityDbContext class inherits from the IdentityDbContext<TUser,TRole,TKey> class residing in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore namespace.
- The
TUserparameter indicates the type of application’s user (AppIdentityUser in this case). - The
TRoleparameter indicates the type of application’s role (AppIdentityRole in this case). - The
TKeyparameter indicates the type of the primary key for users and roles (string in this case).
The constructor of the AppIdentityDbContext class is designed for Dependency Injection support.
Configuring the Startup.js to use Identity
We'll need to amend the Startup.cs to use Identity.
Ensure the Security models are available to the Startup.cs by adding:
Configuring the Startup.cs to use AppIdentityDbContext
Edit the ConfigureServices() method in the Startup.js file. This will allow the use of Dependency injection for the new DbContext of AppIdentityDbContext.
We also need to use services.AddIdentity to add Identity Framework as a service adding the AppIdentityUser and AppIdentityRole classes and indicating where the data will be stored with the AddEntityFrameworkStore() method.
Add the code below the existing AddDbContext for ApplicationDbContext:
The above creates a DbContext for the AppIdentityDbContext as we'll be referencing a different set of a tables. The AddEntityFrameworkStores sets up the application to use ASP.NET Core Identity.
Configuring the Application to use Sessions
Sessions will be used to manage the Identity framework. These need setting up. Firstly as sessions rely on a session cookie, add the following to ConfigureServices(). This will configure the cookie used to manage the session:
Set up the Middleware Pipeline via Configure()
We need to add set up the middleware pipeline to use authentications, authorization and sessions.
Edit the Configure method by adding app.UseAuthentication() and app.UseAuthorization() to the middleware Request Pipeline after the existing app.UseRouting:
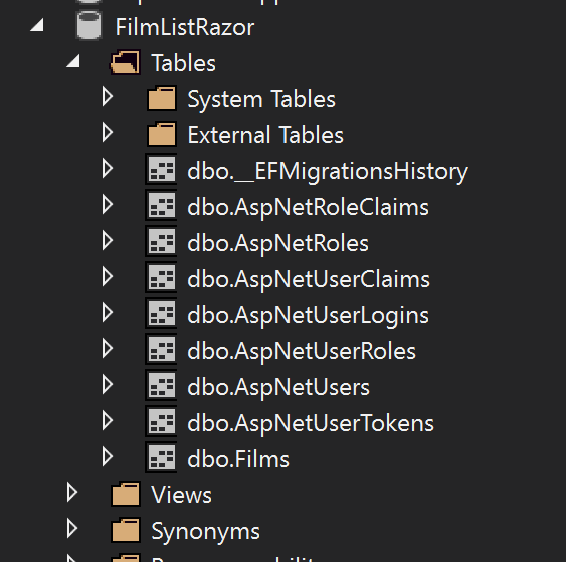
Set Up the Database
Entity Framework can set up the required tables for the Identity to work.
Via NuGet Package Manager > Manage NuGet Packages for Solutions ... install:
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
Use the console to run the migration command and then update the database
add-migration IdentityMigration -context AppIdentityDbContext
Update-Database -context AppIdentityDbContext
Note:
The console commands uses the -context flag to denote the context to mirgrate.
The following tables should now appear: